Data Security and Privacy: A Complete Guide
According to global business advisors at Gartner, 75% of the world’s population will have their personal data regulated by modern privacy laws by the end of the year 2024. As privacy regulations gain momentum across the globe, companies must prepare not only to protect data but also to maintain compliance. Here’s what businesses need to know about data security and privacy.
What Is Data Security?
Data security focuses on protecting data against malicious attacks and threats like data theft, unauthorized access, exploitation, and disclosure. Data breaches remain a major concern for companies and organizations: highly publicized breaches can affect a company’s reputation as well as business operations, client relationships, and even financial stability. Targeted companies may face regulatory fines and legal penalties for compromising consumer data.
Cybersecurity professionals employ several methods to secure data from attacks.
- Data encryption: A cryptographic algorithm encodes data into another form so only authorized persons with a secret key can access or decrypt files.
- Data backup and recovery: Applies disaster recovery (DR) technology like cloud storage or off-site servers to restore original data in case of corruption or breach.
- Masking: Uses a realistic but inauthentic version of the original data to hide sensitive information from hackers.
- Destruction: Ensures data is completely and reliably destroyed from systems to prevent unauthorized retrieval and/or disclosure.
What Is Data Privacy?
Data privacy concerns controlling how data is collected, used, stored, and shared within legal bounds. For consumers, data privacy is the right to determine to what extent organizations use their personal and sensitive information. Data privacy also entitles consumers to the right to be forgotten by companies and/or organizations that store their information.
Data privacy extends to general confidential data such as intellectual property, internal reports, and corporate and legal records, among others.
Data privacy is a direct, logical result of strong data security. When data is safe from misuse and malicious attacks, it is easy to implement protocols around proper, consensual handling of personal information. When security is compromised, however, it’s a lot harder to keep information private.
Nevertheless, data privacy is NOT data security, nor vice-versa. Data security deals primarily with external threats while data privacy involves internal governance of data usage and sharing. While many different industries understand and implement data security as a straightforward concept, the definition of data privacy varies across geographical and legal contexts (e.g., national vs. international consumer privacy laws).
Data Security and Privacy Landscape
Digital transformation has radically altered the playing field for most businesses. Omnichannel readiness, digital customer experience, and dynamic personalization now offer just as much competitive advantage as a company’s products and services. As the consumer-brand relationship becomes increasingly digitized, concern about data privacy and security has incurred a multitude of regulations around the world.
Let’s take a look at how national and international privacy laws are shaping the data security landscape today and what businesses need to do to maintain compliance.
United States
The U.S. has had its eye on consumer data privacy for some time. The coming new year will see a number of bills become state laws, including:
- January 1, 2023: The California Privacy Rights Act and the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act take effect.
- July 1, 2023: The Colorado Privacy Act and the Connecticut Data Privacy Act take effect.
- December 31, 2023: The Utah Consumer Privacy Act takes effect.
These are merely precursors to more privacy bills that are already on the way. A privacy legislation tracker from the International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP) shows active bills from Michigan, New Jersey, Ohio, and Pennsylvania.
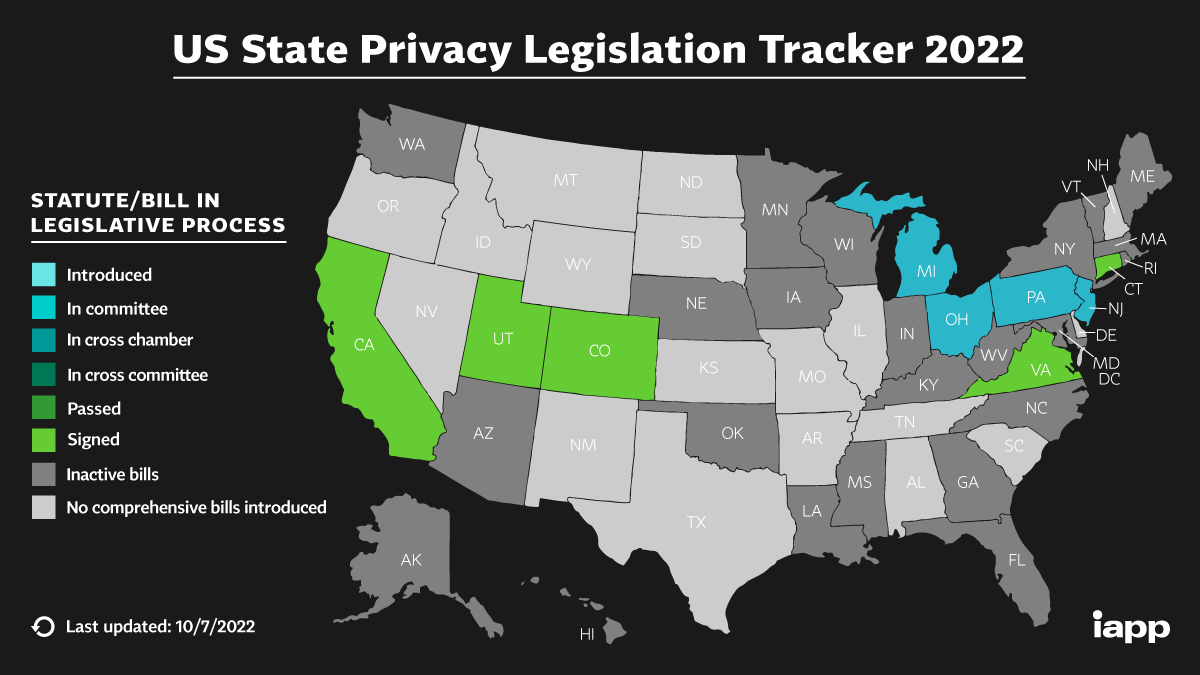
U.S. State Privacy Legislation Tracker from IAPP (Updated October 2022).
These bills grant consumers the right of access, certification, deletion, restriction, portability, and the ability to opt out of sales and automated decision-making. Businesses are obliged to comply with opt-in defaults, transparency requirements, risk assessments, limitations on processing, and discrimination prohibitions.
Europe
Europe is also updating privacy regulations. Major legislative efforts like the Trans-Atlantic Data Privacy Framework (TADPF), Privacy Shield 2.0 updates, and amendments to the French Blocking Institute are focusing on cross-border data requests and transfers. Tighter controls around disclosure will require companies to provide more information to authorities tasked with verifying data access requests.
China
China enacted the Security Assessment Measures for Cross-Border Data Transfers as recently as September 2022. Previously, China has implemented the Cybersecurity Law (2017), Data Security Law (2021), and Personal Information Protection Law (2021). Together with existing privacy laws, the new regulation requires companies to obtain consent and certification for cross-border transfers of data, including personal information.
Proactive Steps Toward Compliance
As privacy laws gain momentum, securing data against cyber threats has never been more important. Below are some proactive steps companies can take to maintain compliance:
Map your data. Understand where your data is located across the organization. Make an inventory of internal and external systems, connected channels, and touchpoints. Identify storage locations/measures for sensitive and personal information. As a best practice, consolidate data silos into a centralized platform for better management. Choose a platform that maps out origin sources as well as where data resides in the consolidated model. It’s also important to use a platform capable of ingesting all types of data that feeds into one place.
Review data protocols and policies. Analyze your organization’s data processing activities to identify protocols that need to be updated to comply with regulations. Verify if data policies like consent options are being implemented by internal teams and whether they are communicated clearly to data subjects. Customer data platforms (CDP) equipped with full consent management modules make it easy for teams to track geo-specific consent rules and implement them in different regions.
Exceed minimum compliance. As privacy laws undergo continuous modifications and updates, they show no signs of relaxing restrictions. Prepare for major regulatory updates by complying with, and—if possible—exceeding minimum standards. Apply best practices to ensure privacy and security. Finally, monitor newly enacted laws as well as bills under discussion in various legislatures.
Data Privacy Solutions
Data privacy solutions keep sensitive information private and protected. They serve the double purpose of preventing unauthorized access and protecting businesses from receiving regulatory fines.Three data privacy solutions to consider when securing sensitive data include:
- Data and file monitoring tools. These devices monitor activity around data assets and important files. They alert administrators to suspicious behavior patterns or logins from questionable accounts. Early detection prevents further risk or damage to data assets.
- Risk analysis tools. These instruments analyze and evaluate privacy risks in a company’s data management process. Such risks include inadequate security safeguards, malware and viruses, access by external parties, outdated systems, lack of encryption, and others. Risk analysis tools identify vulnerabilities along the data lifecycle, from collection to storage and usage. For multinational companies, analysis may also include risk factors during international data transfers.
- Automated compliance monitoring. These solutions automate compliance monitoring by continuously tracking where data (like personally identifiable information or PII) reside in a company’s systems. Once sensitive information moves beyond established protocols, automated compliance monitoring tools alert administrators to take action. Advanced tools can also confirm if requirements and data policies are up to date to maintain compliance.
Data Governance
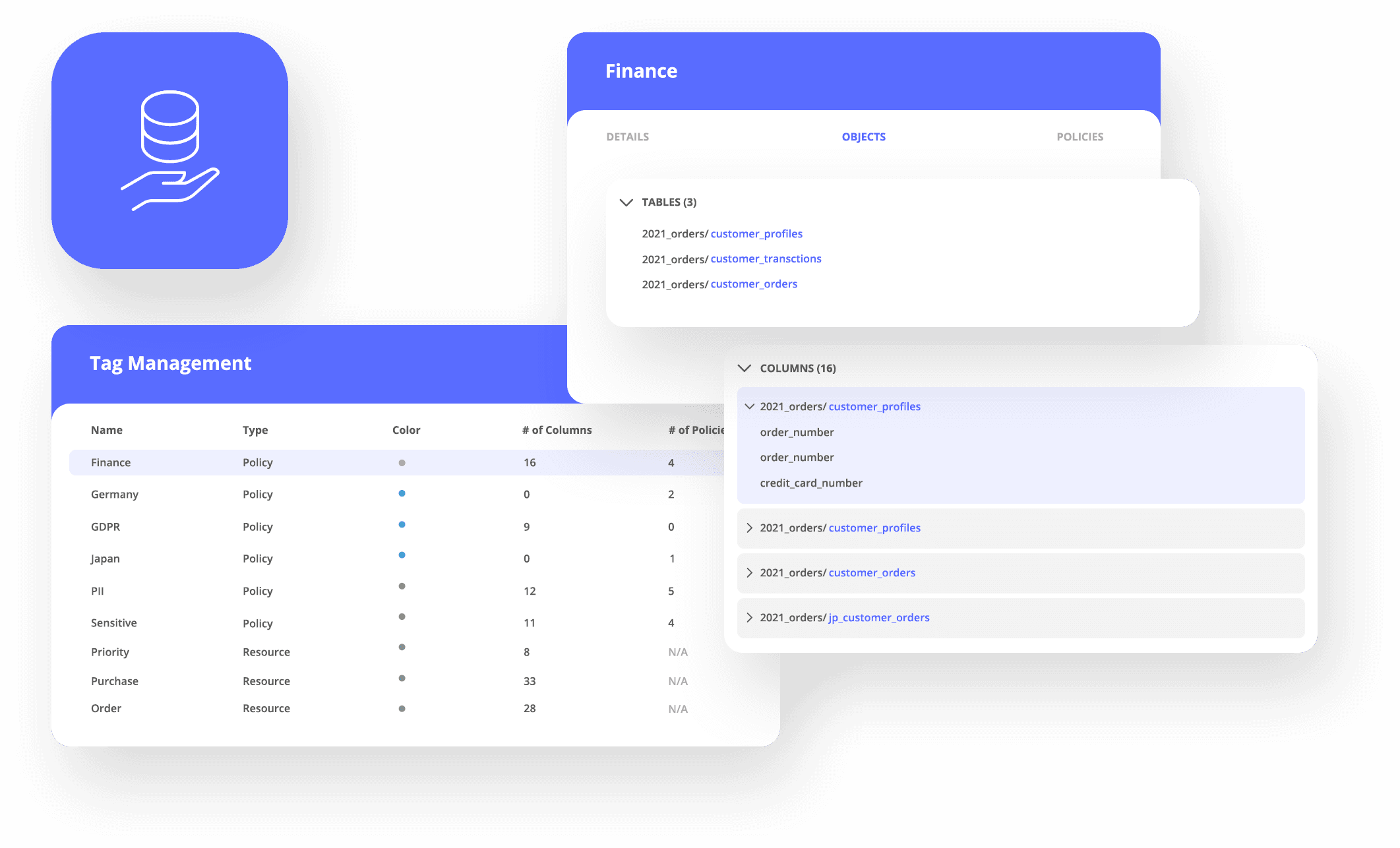
Contemporary data governance has become incredibly complex due to the sheer amount of data generated by customers via digital channels and touchpoints. To keep up with ever-widening data streams and tightening privacy regulations, companies need a solution to simplify the governance of data security and privacy. A customer data platform (CDP) solves these challenges by centralizing data and control in a single location.
CDPs eliminate data silos. A CDP stores all customer data—from websites to offline records to CRMs and more—in one place. Centralized data storage also eliminates piecemeal data governance solutions that may overlook loopholes in data privacy and security.
A CDP centralizes control. Data administrators can manage access and permissions using a single platform, increasing transparency and accountability around data use.
A CDP unifies customer profiles. Teams can use a CDP’s profile unification capability to track customers’ actions as well as their consent and preferences. Unified profiles also enable teams to fulfill data subject access requests (DSARs) on demand.
Ensuring Data Security and Privacy With Treasure Data’s CDP
Treasure Data Customer Data Cloud helps you earn and keep your customers’ trust through data security and privacy compliance. Our enterprise-grade CDP gives you a single, powerful platform to collect data with consent anywhere, enforce and maintain privacy compliance, and adapt to changing regulations quickly and easily.
Collect Every Data Point With Geo-Specific Consent
Treasure Data collects, secures, and activates every piece of customer information with consent across all channels, teams, and brands—wherever they may be.
Govern Data in One Place
Treasure Data unifies all of your data with consent in a centralized platform so you can govern access, enable audit logs, and pick out suspicious activity easily.
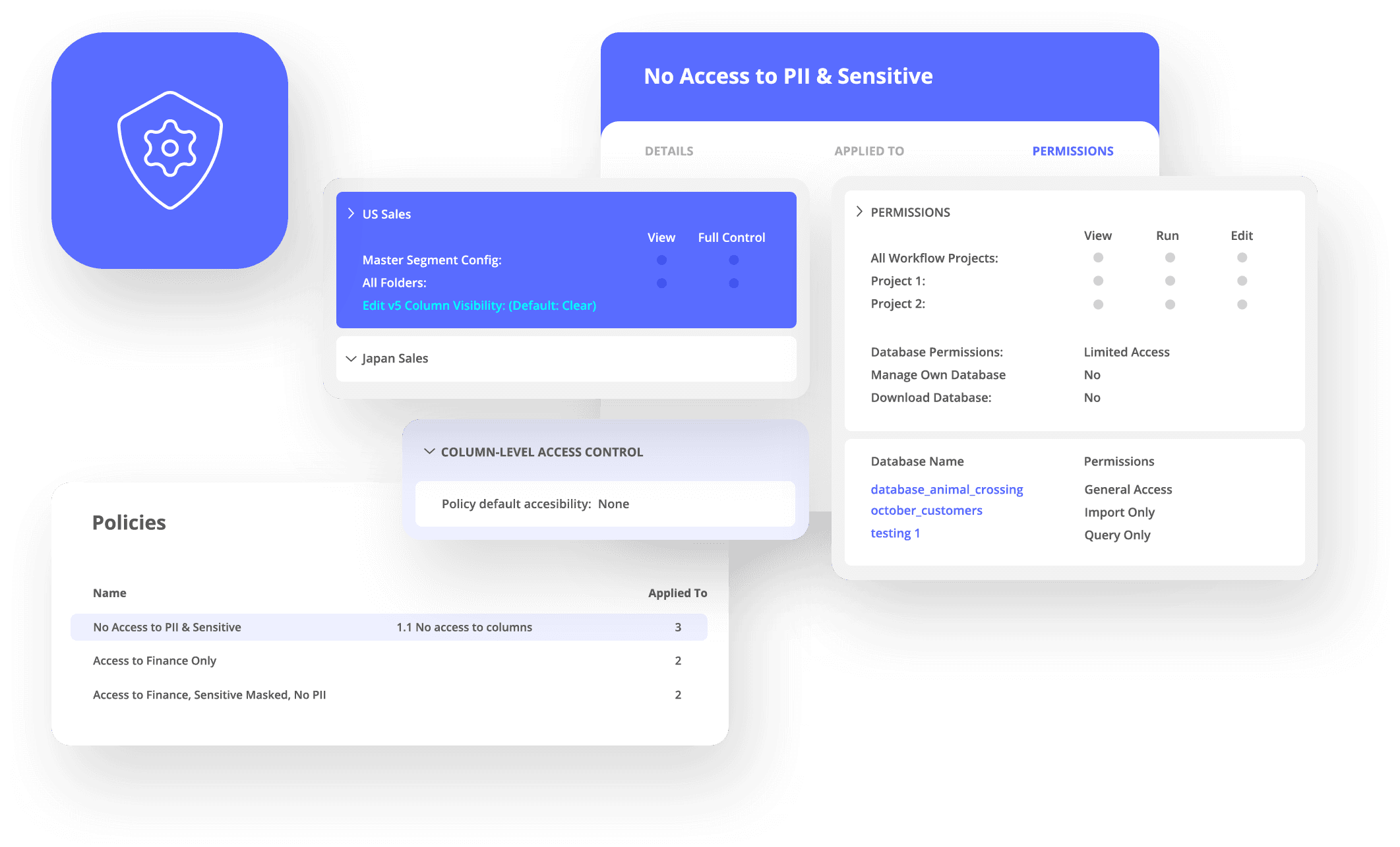
Manage Security and Privacy
Use Treasure Data Customer Data Cloud to restrict access to Personally Identifiable Information (PII), and handle automated workflows for DSARs and privacy requests. Enforce consent management, log data use, and manage emergencies from Treasure Data’s secure platform.
Treasure Data complies with the latest regulations and continually builds on a strong data security foundation.
Treasure Data Customer Data Cloud is an integrated suite of cloud-based customer data platform solutions. Treasure Data provides insight by collecting and centralizing customer data, unifying profiles, and analyzing journeys to surface hidden trends in customer behavior.
See Treasure Data’s enterprise customer data platform in action below:
To learn more about how you can use Treasure Data’s CDP to ensure data security and privacy, consult an expert today. Want to learn more? Request a demo, call 1.866.899.5386, or contact us for more information.
